What is and how to configure reverse DNS?
As a preventive measure against overload during the delivery of the email, it is essential to ensure that the reverse DNS data has been filled it and configured correctly. Most often, the reason for setting up a reverse DNS registration is to add credibility to the e-mail server handling outgoing messages. Reverse DNS provides additional tracing to the origin of an email as some incoming email servers will not receive any messages unless the originating IP has a reverse DNS configured. This article details how to configure a reverse DNS area suitable for improving the email messages delivery.
What is Reverse DNS?
Reverse DNS (rDNS) is a name resolution searching an IP address in order to obtain a domain name, thus fulfilling the reverse function of the DNS server, which transforms the domain names into IP addresses.
Reverse DNS can be used as a spam filter. Usually, spam generator users utilize a nonvalid IP addresses, meaning an IP addresses that does not match a certain domain name. A reverse DNS software looks for the IP address of a message that was received and if it does not find it, the message is blocked by the server. Although reverse DNS is fairly efficient in filtering spam messages, many times valid email messages are also blocked.
Configuration stages for the Reverse DNS
You have to create a reverse DNS of the DNS authorized name server for the main IP address of your server. In order to do that, follow these steps:
1. Log into your My Maghost account by accessing the link HERE
Note: Use your login data correctly. If you are unable to login, please contact Maghost Help Center.
2. Once you have logged into the admin page, access the upper menu Domains > Manage DNS
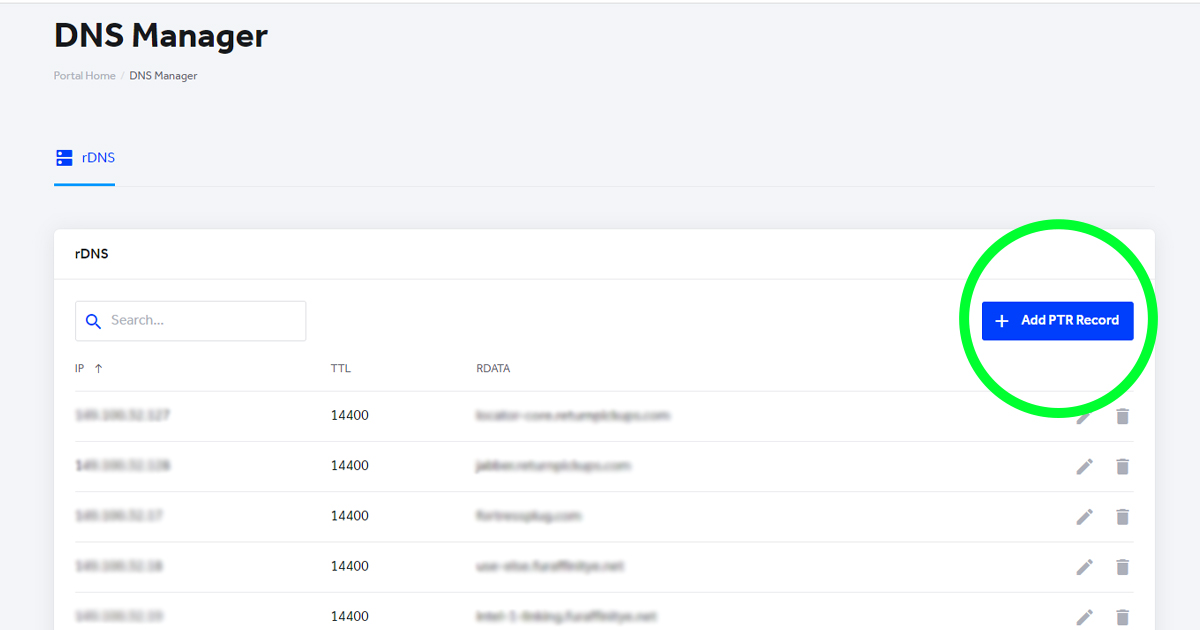
This page contains all existing Reverse DNS servers.
3. In order to configure a new Reverse DNS server, click on ADD PTR.
4. In the new window we have the following fields:
Related Item: choose the desired service
IP Adress: choose the IP address
TTL: A 32 bit signed integer that specifies a time interval that the resource record may be cached before the source of the information should again be consulted. Zero values are interpreted to mean that the RR can only be used for a transaction in progress, and should not be cached.
RDATA: PTRD name
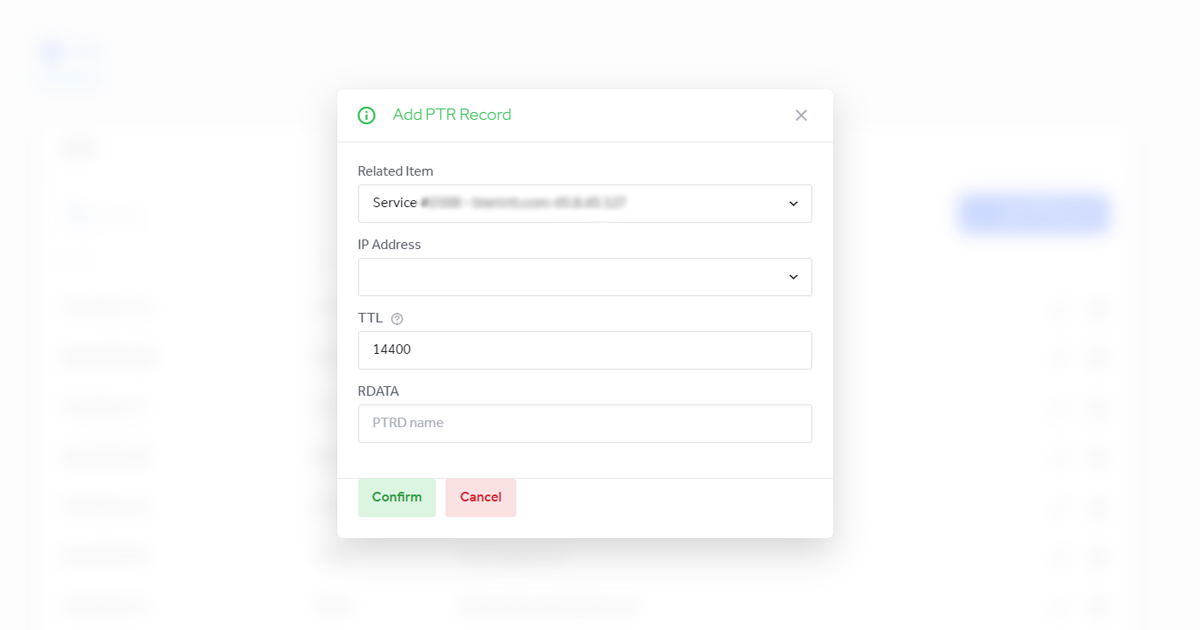
After completing the form, press the ADD button to save the new PTR.
That’s Easy, Right? 😉


